学习学长的idea
Mask-TS
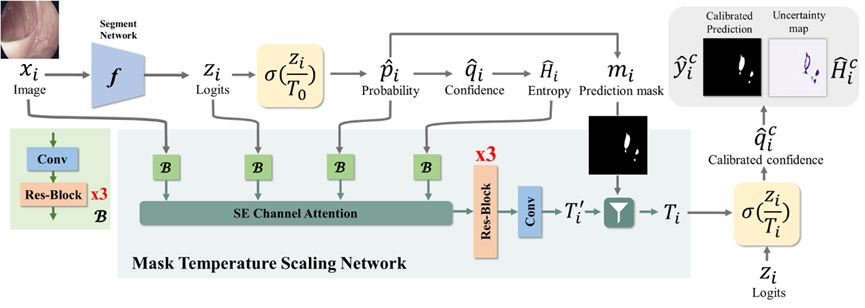
将原图、模型输出logits、概率图、不确定性图分别输入到4个一样的卷积网络当中,4个通过卷积之后代表它们考虑了像素点之间的位置关系。(只要通过了卷积网络就已经考虑了像素之间的位置关系)这四个卷积的输出放入一个注意力通道当中,通过自适应权重进行相加。
Hi和Pi这两个分支分别在增强边缘形状和更仔细地处理预测的真值方面发挥了作用,而x i包含丰富的原始信息,z i拥有与分割有关的特征,因为它源于一个分割网络
被认为是背景的部分就保持原始全局T0不变,被认为是病变区域的就用校准之后pre-output T‘。
Mask-loss
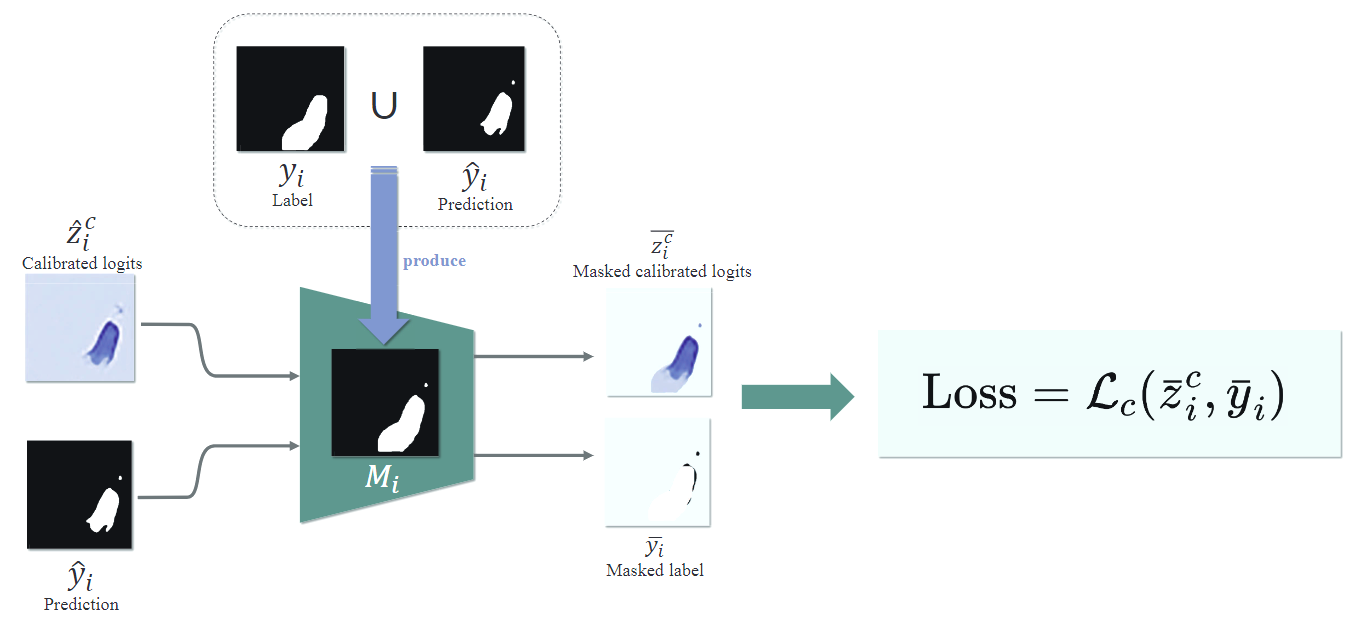
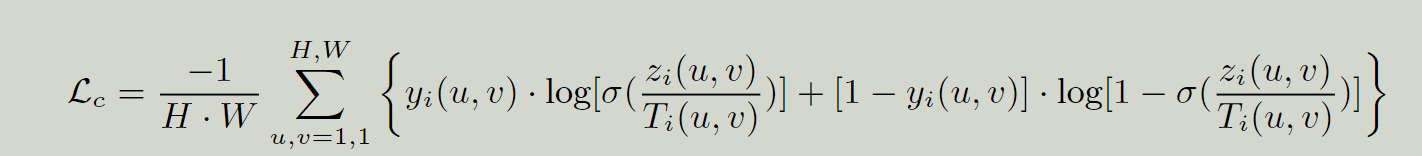
先将label和prediction合并,然后将calibrated logits的背景视为白色,忽略掉背景,将prediction黑白反转。再将两图合并,得到一个关注边缘的图像。再利用的二分类交叉熵损失函数。
confidence and accuracy
In learning algorithm, Confidence defines the probability of the event (or probability of input to fall in different classes).
If a class has high probability then it has high confidence. Confidence value can be calculated for single input as well giving the meaning as how much the algorithm is confident for that class.
On the other hand, accuracy defines the skill of the learning algorithm to predict accurately. It defines the percentage of correct predictions made from all predictions.
ECE是越小越好
ODC-SA Net
to deal with multi-directional features and drastic changes in scale.多方向的特征和规模的急剧变化。
existing problems
In the target images containing extremely hidden polyps, the angles of them change randomly with the movement of the lens, which makes the features of the polyps no longer representative in a fixed or specific few directions.在含有极度隐藏的息肉的目标图像中,它们的角度随着镜头的移动而随机变化,这使得息肉的特征不再代表固定或特定的几个方向。
The size of the hidden object in the polyp image varies dramatically息肉图像中隐藏物体的大小变化很大
Most of the existing methods ignore the importance of feature reorganization after the multi-layer feature fusion operation for the segmentation problem, which makes the rich semantic information obtained by the encoder cannot be fully utilized.现有的方法大多忽略了多层特征融合操作后的特征重组对分割问题的重要性,这使得编码器获得的丰富语义信息不能得到充分的利用。
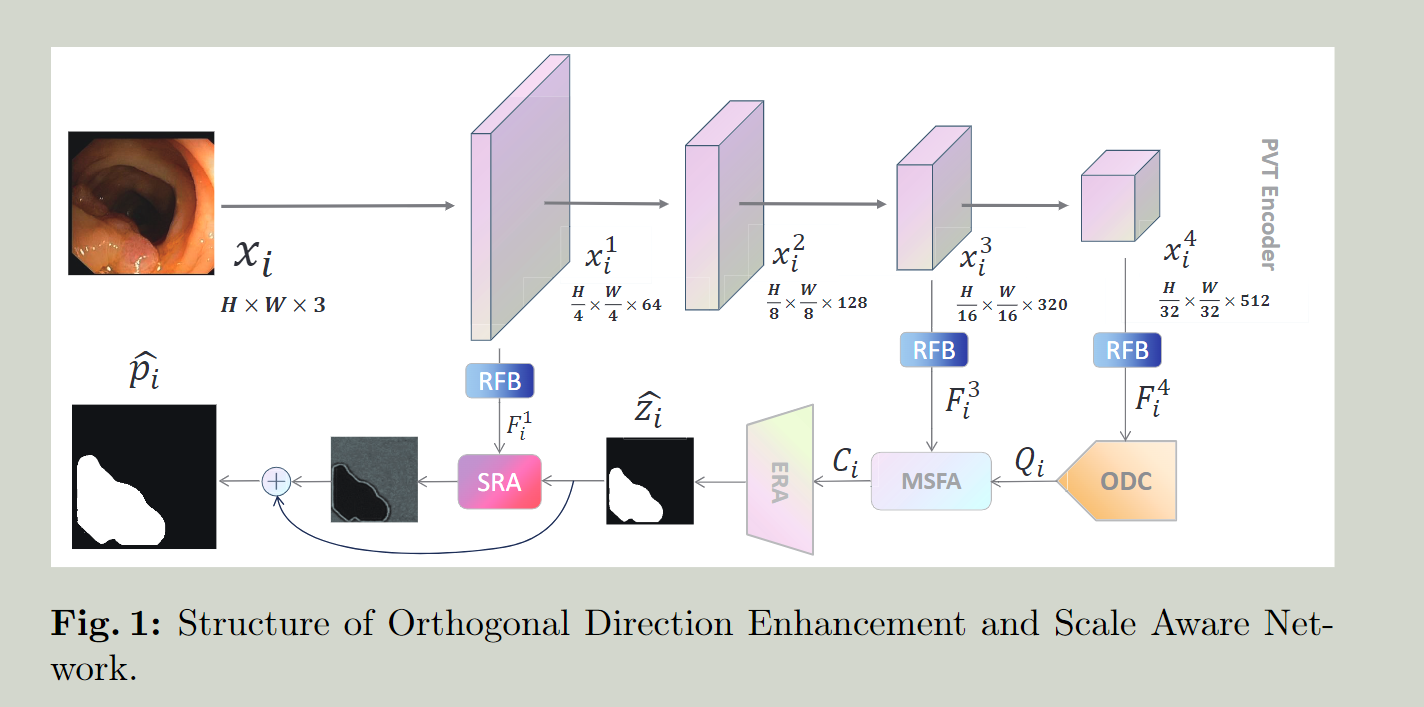
ODC:Orthogonal Direction Enhancement 正交方向增强
正交方向卷积(ODC)块可以通过形成正交特征向量基础,利用转置的矩形卷积核提取多方向特征,解决了随机特征方向变化的问题,减少了计算负荷。
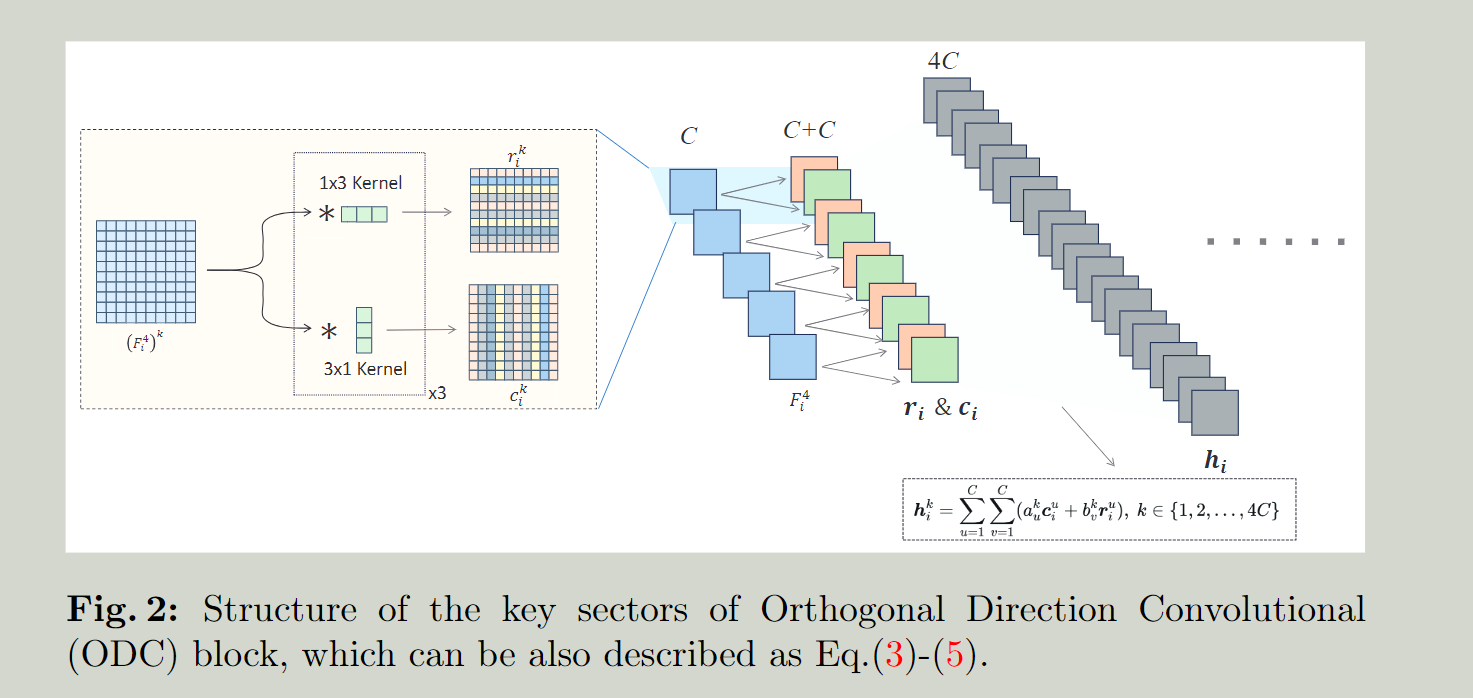
需要解决的问题:
different location and shooting direction of the colonoscopy-lens, the usual convolution kernel will miss features in specific directions due to the rotation of the image or the target because of its square shape and fixed sliding direction
由于结肠镜-透镜的不同位置和拍摄方向,通常的卷积核会因为图像或目标的旋转而错过特定方向的特征,因为它是方形的,而且滑动方向固定。
solves the problem of random changes in target feature directions?
解决方法:
一对转置矩形卷积核(1×3和3×1)分别提取最深层图像的每个通道的垂直和水平的特征来形成一个正交特征基准
每个通道特征可以用一个线性表达式来表示:
网络下一层的任何通道的特征图应该是上一层的所有通道与任何方向的特征的组合
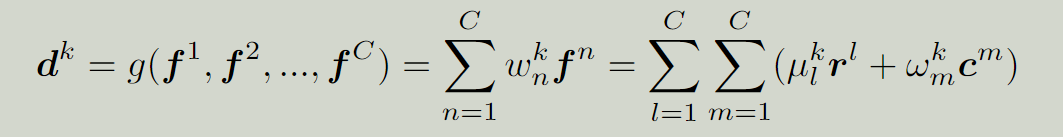
具体操作:
一个三层的1×3卷积去提取水平特征 另一个三层的3×1的卷积去提取垂直特征
然后将这两个特征通过线性组合合并得到
最后再进行一个残差连接,把原图接进来,得到
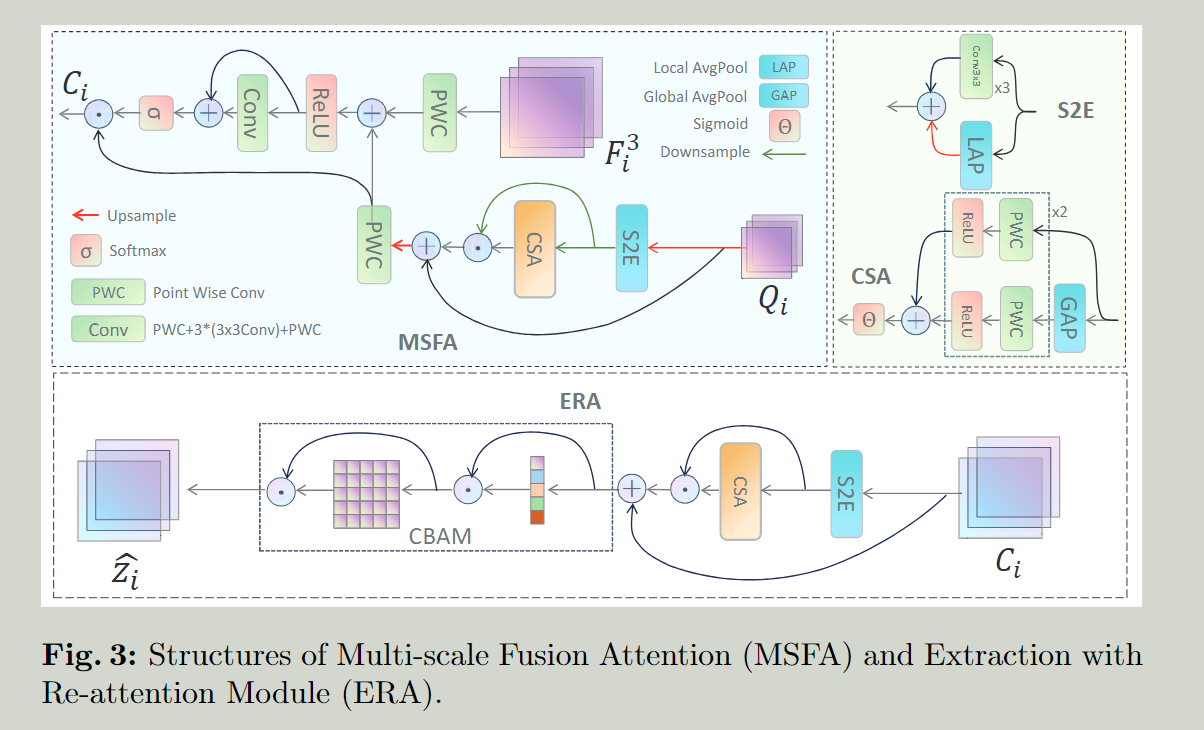
SA: Scale Aware 扩大感受野 MSFA
Multi-scale Fusion Attention mechanism 多尺度融合注意(MSFA)机制
emphasize scale changes in both spatial and channel dimensions, enhancing the segmentation accuracy for polyps of varying size 强调了空间和通道维度上的尺度变化,提高了不同大小的息肉的分割精度。
需要解决的问题:
The growth time of polyps in the intestine, the environment and the shooting distance of the colonoscopy lens are different. The polyps contained in the pictures have different sizes, and their color and texture characteristics are very similar to the background.
息肉在肠道、环境中的生长时间和结肠镜镜的拍摄距离是不同的。图片中包含的息肉有不同的尺寸,它们的颜色和纹理特征与背景非常相似。
Most of the existing methods treat scale-varying features as the same and ignore the attention bias caused by their differences in spatial and channel dimensions.
大多数现有的方法将标度变化的特征视为相同,而忽略了由它们在空间和通道维度上的差异引起的注意力偏差。
解决方法:
提出Spatial Scalable Enhancement Mechanism (S2E) and Channel Scalable Attention Mechanism (CSA)
S2E增强多尺度的空间特征,CSA在通道维度增强多尺度注意力
expand the receptive field in both spatial and channel dimensions by convolutional and pooling parallel dual channels of the high-level feature map Q i containing more semantic information, and use the feature map of the lower layer x3 i , which has more detail information than Q i , to give attention to the deep semantics of objects with different sizes to de-emphasize the influence of background and interference
通过卷积和池化并行的双通道方式扩大高等级特征图在空间和通道两个维度上的感受野,并使用包含更多详细信息的底层特征的增加对于深层语义分割不同大小的注意力,降低对背景的关注。
S2E:Spatial Scalable Enhancement Mechanism 空间可扩展的增强机制
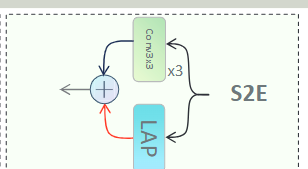
双线并行
一个是包含3个3*3的卷积层,可以获取局部特征信息并通过卷积操作增强其对于小物体的特征信息。
另一个是一个平均池化层,在一些特定区域(2*2大小),平均池化可以保留大目标,减弱小目标(由于更大的目标包含更多的像素点),这样之后新特征图的总体分布和大目标的分布更接近,同时也获得了全局的上下文信息。
它减弱了空间分辨率但增强了全局上下文信息在没有增大计算量的前提下。
在平均池化之后,插值被放大(没有对小物体的削弱进行补偿)来保证和第一个通道上的图片大小一致,并且相加。
这样可以做到融合了空间多尺度信息,同时不用很大的计算量。
Output:
CSA:Channel Scalable Attention Mechanism 通道可扩展注意机制
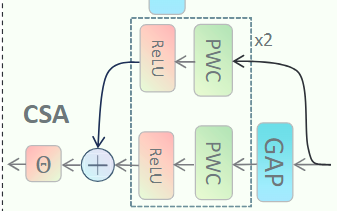
要解决的问题:Different channels contain different semantic information, and there are scale differences in the targets mapped by these channels.不同的通道包含不同的语义信息,这些通道映射的目标也存在规模差异。
对于小目标:传统的 Point-Wise-Conv + ReLU 提升注意力
对于大目标:先进行平均池化之后再进行 Point-Wise-Conv + ReLU 利用每个通道特征图的像素平均值,在全局信息的引导下获得通道注意力,增加了大尺度特征图的权重
两个分支的输出相加送入Sigmiod得到输出,之后和相点乘之后再和相加得到 ?学长好像写错了,应该是先和Si点乘之后再和Qi相加
Output:
RFA:Residual Fusion Attention 剩余融合注意
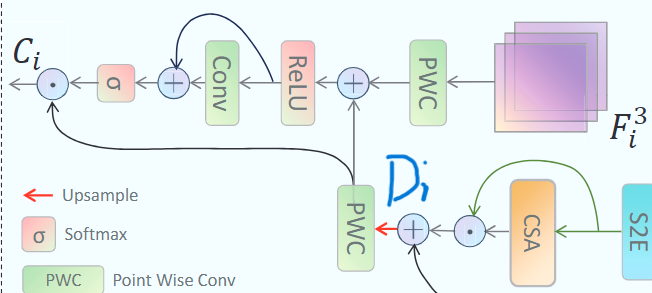
通过 来指导 进行浅层和深层特征融合。
这里经过上采样和驻点卷积使得和大小一样,同样也经过逐点卷积得到相同大小,相加之后经过一个ReLU激活函数和一个Conv block ,之后再进行一次残差连接,最后的通过softmax输出的包含了每个像素的有效信息。最终再和上采样之后的点乘,自动关注目标区域。
Output:
Extraction with Re-attention Modul (ERA)
re-combine effective feature 重新组合有效的特征
两组通道和空间注意机制用来提取经过多层特征融合之后的深度语义信息。特征重新提取和权重分配更好地利用语义信息并防止细节被忽略。
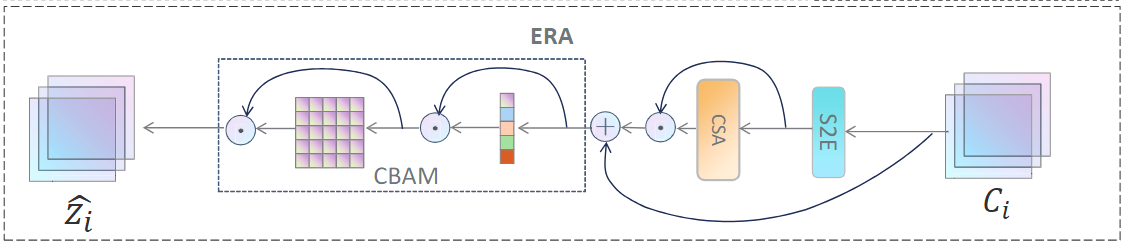
further adjust and integrate its own feature information. This process generates a feature enhancement and combination graph that is more in line with the target. It allows different features to be combined into better features and can also realize the allocation of different feature emphasis degrees.
进一步调整和整合自己的特征信息。这个过程产生了一个更符合目标的特征增强和组合图。它允许不同的特征被组合成更好的特征,也可以实现不同特征强调程度的分配。
实现更好的拟合。
Output:
Shallow Reverse Attention Mechanism (SRA)
enhance polyp edge with low level information 用低层次的信息增强息肉边缘
渐层的编码输出有较多的边缘信息,指导RA(Reverse Attention)增强分割目标。
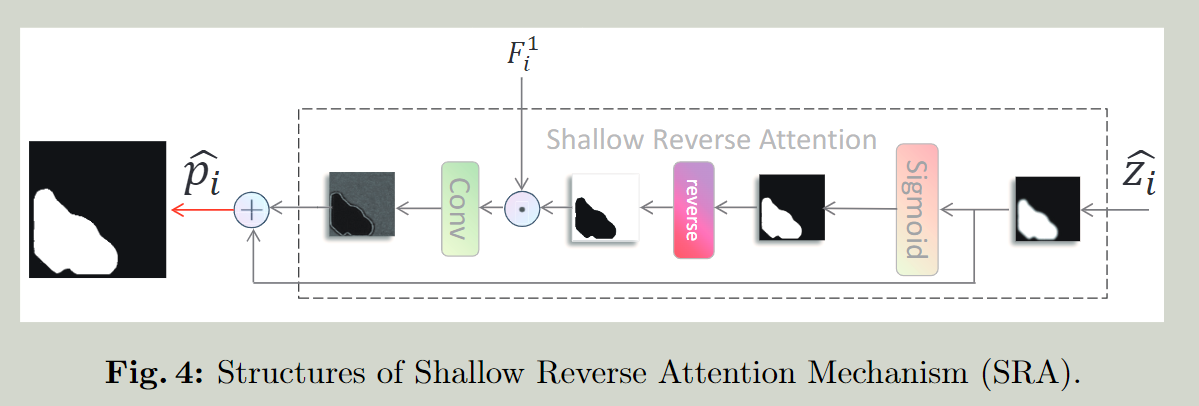
problems:
the boundary between the background and the target is not obvious
solutions:
Inspired by ParNet, introduce RA (RA exploits the details of complementary regions by erasing the polyp regions that have been judged RA通过擦除已经判断过的息肉区域来利用互补区域的细节)
我们的网络使用最浅层的特征图来进行边界增强。
Output:
Loss function
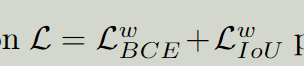
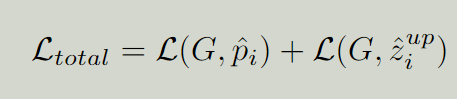
使用deep supervision 上采样到和一样大,也一样。
Reference:
【机器学习】详解 转置卷积 (Transpose Convolution)-CSDN博客
增强感受野SPP、ASPP、RFB、PPM_spp模块的作用-CSDN博客
markdown中的特殊字符、数学公式、图表等语法总结_markdown 制作流程图 有特殊符号-CSDN博客
markdown公式中字母加粗_markdown 公式加粗-CSDN博客
Latex所有常用数学符号整理_latex数学符号-CSDN博客
Depthwise卷积与Pointwise卷积-CSDN博客
通俗易懂理解注意力机制(Attention Mechanism)-CSDN博客
Pyramid Vision Transformer(PVT): 纯Transformer设计,用于密集预测的通用backbone-CSDN博客